Do it yourself NCL Script Examples
There is no way we can demonstrate every nuance of NCL on this page. You will also need to use the CCSM Graphics Examples to truly learn NCL.
Cylindrical Equidistant Plots
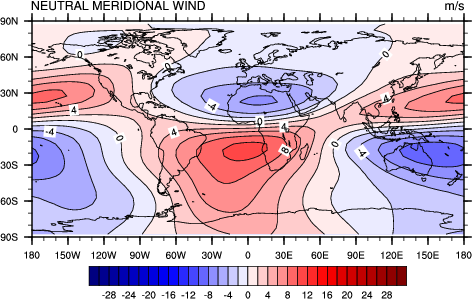
ce_1.ncl:
Default black and white plot.

gsn_csm_contour_map_ce is the plot interface that creates a cylindrical equidistant plot. cnLineLabelPlacementMode = "constant", is one of the three methods for controlling contour labels. the constant method is the only one in which the label becames part of the line. There are four title strings you can use to label a plot. The gsnLeftString is automatically labeled with the long_name of the data, and gsnRightString is labeled with the units of the data. These can both be overwritten, or turned off (by setting them to ""). There is also gsnCenterString and the plot title tiMainString. |
ce_2.ncl:
Adds color and a local time axis.
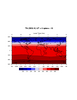 cnFillOn = True, turns on a color plot. gsnSpreadColors is a special resource that tells the plot template to use the full range of the colormap. There are many built-in colormaps to choose from and many ways of specifying the color of a plot. axis.ncl contains all the functions used to put local time axis on the HAO master scripts. We have used one of those functions here (set_lt_axis_ceplot). To use this function, you need to load axis.ncl at the top of your script. Note that this function turns off gsnLeftString and gsnRightString. |
ce_3.ncl:
Demonstrates the use of a
shea_util special contour effects function. There are numerous
other
contour effects to choose from.
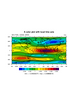 ZeroNegDashLineContour draws negative contours as dashed
and the zero line as double thickness.
ZeroNegDashLineContour draws negative contours as dashed
and the zero line as double thickness.
The NCL built-in functions min and max allow you to take the min and max of the data. |
ce_4.ncl:
Demonstrates manually setting contour intervals
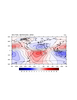 cnLevelSelectionMode = "ManualLevels"
cnLevelSelectionMode = "ManualLevels"cnMinLevelValF cnMaxLevelValF cnLevelSpacingF are the resources that manually sets the contour levels. cnLineLabelsOn turns on the contour line labels, while cnLineLabelBackgroundColor controls the color behind the label. The gsn_csm templates set this to transparent by default. You can not use this resource if you set cnLineLabelPlacementMode to "constant". |
ce_5.ncl:
Demonstrates plotting data on magnetic coordinates
 The function mag2latlon (found in
hao_cobntrib.ncl takes data
on magnetic coordinates and changes the named dimensions fixes
the units of the coordinate variables so that the NCL gsn_csm plot
interfaces do not produce error messages.
The function mag2latlon (found in
hao_cobntrib.ncl takes data
on magnetic coordinates and changes the named dimensions fixes
the units of the coordinate variables so that the NCL gsn_csm plot
interfaces do not produce error messages.It is necessary to turn off the cyclic point by setting gsnAddCyclic to False. The gsn templates automatically add a cyclic point, and data on the magnetic coordinates already has one. The local time axis for data on the magnetic grid is on the bottom replacing the longitude axis. |
ce_6.ncl:
Demonstrates overlaying an apex coordinate grid
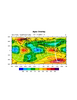 This involves the creation of two overlays, one of the apex lat/lon
and the other of the combined apex lat/lon and the original plot.
Please see script for details.
This involves the creation of two overlays, one of the apex lat/lon
and the other of the combined apex lat/lon and the original plot.
Please see script for details.
|
ce_7.ncl:
A real world example of a customized plot. This example includes
the addition of vectors, explicit contours, and map zooming.
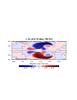 mpMinLatF and
mpMaxLatF will zoom in the map.
mpMinLatF and
mpMaxLatF will zoom in the map.Sometimes when only the latitude axis is limited, the labels shrink to the point that they are unreadable. We can blow them up using tmXBLabelFontHeightF and tmYLLabelFontHeightF. It may also be necessary to enlarge so the the general text with txFontHeightF. To effectively view the variable in this example, it was necessary to explicitly set the contour intervals. This is done with cnLevelSelectionMode = "Explicit" and providing values to cnLevels. This example draws vectors on top of scalars. For a complete description of the vector resources used, and other vector options, please check out the CCSM vector page |
ce_10.ncl:
Demonstrates a panel plot. There are too many nuances associated with
panelling. Please review the CCSM panel example page for details.
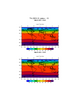 gsnZonalMean = True will turn on a side zonal mean plot on cylindrical equidistant plots only. |
ce_11.ncl:
Demonstrates interpolating the data to height before plotting.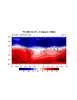 hao_contrib.ncl contains the function "zplev_to_height" which we use to interpolate to height in the master scripts. Note that this function requires the create of a logical variable to which you attach the height value. In the master scripts this variable is also used for other things. |